Aim: Warfarin, which is widely used for preventing thromboembolic events, can cause major and minor side effects. The aim of this trial is to evaluate the effect of nurse home-support program on self-management of patients receiving warfarin therapy.
Method: A randomized, controlled trial was conducted using 36 selected and eligible patients who had 12-month home-visit follow-ups. The bleeding risk score, potential and preventable warfarin-related complications, patients’ self-management behaviors, and anticoagulation satisfaction were examined. Data analyses were performed using parametric and nonparametric tests, split-plot analysis of variance, multiple regression analysis, and Bland and Altman plots test.
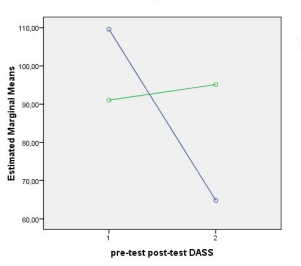
Results: The bleeding risk score was an effective variable for assessing patient satisfaction (p<0.05). The self-management group demonstrated decreased bleeding risk at the end of the trial. The Duke Anticoagulation Satisfaction Scale mean score represents a statistically significant improvement in the self-management group (p<0.05). Patients’ self-management behaviors improved significantly in the self-management group compared to the control group (p<0.05). The number of international normalized ratio values within the target range was significantly higher in the self-management group (174/432) than in the control group (82/432). The self-management group showed significant reductions in both thromboembolic events.
Conclusion: This trial demonstrated evidence that use of nursing home care is effective in developing self-management behaviors, improving patient satisfaction, and preventing complications in patients receiving warfarin therapy. This model could be easily adopted and implemented by home care services and health organizations.
Cite this article as: Yıldırım, J. G., Bayık-Temel, A. (2020). The effect of nurse home-support program on self-management of patients receiving oral anticoagulation (Warfarin) therapy. Florence Nightingale Journal of Nursing, 28(1), 13-22.




.png)
.png)